How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. Understanding the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvering techniques, is crucial for both safe and successful flights. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to confidently take to the skies.
This comprehensive guide delves into every aspect of drone operation, starting with a thorough understanding of the drone’s components and their functions. We’ll then walk you through essential pre-flight procedures, ensuring your safety and the drone’s well-being. Mastering takeoff and landing techniques, understanding drone controls, and navigating various flight modes will be covered in detail, culminating in techniques for capturing stunning aerial imagery and managing your drone’s battery effectively.
Finally, we will address legal considerations and troubleshooting common issues, preparing you for a rewarding experience with your drone.
Drone Components and Their Functions: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the individual components of a drone and how they work together is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the major components, their functions, and their interaction during flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety regulations and proper procedures. For a comprehensive guide on the subject, refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic flight maneuvers to advanced techniques.
Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation comes down to consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Drone Component Descriptions and Interactions
A drone’s flight relies on the coordinated function of several key components. These components work in synergy to provide lift, stability, control, and data acquisition.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, pushing air downwards to lift the drone. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, the flight controller receives data from various sensors and uses algorithms to maintain stability and execute pilot commands. It regulates motor speed and direction to achieve desired movements.
- Battery: The power source for the entire system. LiPo (Lithium Polymer) batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density. Battery life significantly impacts flight time.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): A GPS module provides location data, enabling features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and precise positioning. It’s essential for autonomous flight modes.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. Modern drone cameras often include features like adjustable aperture, shutter speed, and ISO settings for image quality control.
During flight, the pilot’s commands are processed by the flight controller. The flight controller then adjusts the speed of each motor individually, altering the thrust produced by the propellers. The GPS provides location data, helping the flight controller maintain position and execute autonomous functions. The camera captures the visual data.
Drone Component Specifications Comparison
| Component | Specification Example | Functionality | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propeller | 8 inch, 5-blade | Lift generation, thrust control | Size and blade count affect thrust and efficiency. |
| Motor | 2204 2300KV Brushless | Powering propellers | KV rating indicates motor speed. |
| Flight Controller | Pixhawk 4 | Flight stabilization, data processing, command execution | Different controllers offer varying levels of features and capabilities. |
| Battery | 1500mAh 3S LiPo | Power supply | mAh indicates capacity, S indicates cell count (voltage). |
| GPS | uBlox M8Q | Position and navigation data | Accuracy varies depending on satellite signal strength. |
| Camera | 4K UHD, 3-axis gimbal | Image and video capture | Resolution and gimbal stabilization affect image quality. |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight inspection is critical for safe drone operation. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents and equipment damage. This section Artikels essential pre-flight procedures.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
Before each flight, carefully review this checklist to ensure your drone is in optimal condition.
- Inspect propellers for damage or wear.
- Verify battery charge level and health.
- Check motor function and responsiveness.
- Confirm GPS signal acquisition and accuracy.
- Inspect camera functionality and settings.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Review local airspace regulations and restrictions.
- Check weather conditions for safe flight.
- Ensure adequate visibility and clear flight path.
Sensor Calibration and Safety Protocols
Calibrating the drone’s sensors, particularly the compass and IMU, is vital for accurate flight performance. This process ensures that the drone’s internal orientation and position data are correct. Failure to calibrate can result in erratic flight behavior.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Successfully navigating the airspace requires mastering takeoff, flight maneuvers, and safe landings. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and become a confident pilot. Proper training is crucial before operating any drone responsibly and safely.
Safety protocols should include understanding emergency procedures such as battery failure, GPS loss, and unexpected malfunctions. Having a plan for these scenarios can minimize risk and potential damage.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are essential for preventing accidents. This section describes different techniques and considerations for various conditions.
Takeoff Procedures
A smooth and controlled takeoff is crucial. Begin by ensuring the drone is in a stable, level position. Select the appropriate takeoff mode (assisted or manual), and gently increase throttle to initiate ascent. Maintain visual contact throughout the process.
- Assisted Takeoff: Uses GPS and other sensors to aid in a stable lift-off.
- Manual Takeoff: Requires more skill and control from the pilot.
Landing Procedures
A smooth landing involves a gradual descent, maintaining control and stability. Reduce throttle slowly to decrease altitude, ensuring a gentle touchdown. Keep the drone level and avoid sudden movements.
- Begin descent slowly.
- Maintain visual contact with the landing area.
- Adjust throttle smoothly to control descent rate.
- Execute a gentle touchdown.
- Power down the drone.
Wind Conditions
Wind can significantly impact takeoff and landing. Strong winds may require postponing flight. In moderate winds, take off and land into the wind to maintain stability. Adjust throttle and control inputs accordingly to compensate for wind gusts.
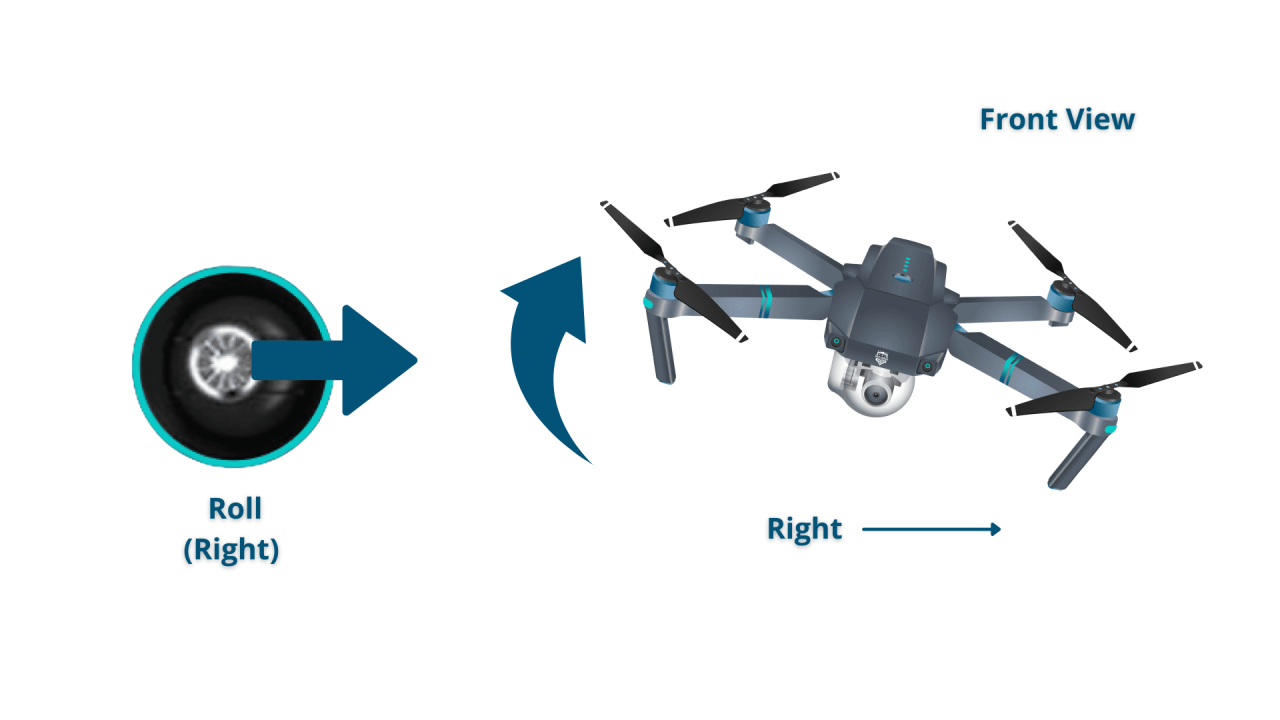
Drone Controls and Maneuvering
Understanding drone controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains control schemes and basic maneuvers.
Drone Controller Functions
Most drone controllers use two joysticks. The left joystick typically controls altitude and direction, while the right joystick controls pitch and roll. Buttons are used for various functions like taking photos/videos, returning to home, and selecting flight modes.
Control Schemes (Mode 1 vs. Mode 2)
Mode 1 and Mode 2 refer to the joystick assignments. In Mode 1, the left stick controls yaw and throttle, and the right stick controls pitch and roll. In Mode 2 (the more common scheme), the left stick controls pitch and roll, and the right stick controls yaw and throttle. Familiarity with the chosen mode is crucial.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
The following flowchart illustrates basic maneuvers:
(A textual representation of a flowchart would be provided here, illustrating the steps involved in hovering, ascending, descending, yawing, pitching, and rolling. This would include directional stick movements and throttle adjustments for each maneuver.)
Precise Drone Control and Stabilization
Precise control involves making small, smooth adjustments to the joysticks. Practice is key to mastering this. Features like GPS stabilization and assisted flight modes can aid in maintaining stability, especially for beginners.
Drone Flight Modes and Settings
Different flight modes and settings provide varying levels of control and autonomy. Understanding these is essential for adapting to different environments and situations.
Flight Modes and Settings
- GPS Mode: Relies on GPS for position holding and stability. Ideal for stable hovering and precise movements.
- Atti (Attitude) Mode: Relies on onboard sensors for orientation and stability. Useful for indoor flight or areas with weak GPS signals.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point. Crucial for safety and recovery.
- Sport Mode (or similar): Offers increased responsiveness and speed. Requires more skill and experience.
- Manual Mode: Provides full control to the pilot. Most demanding mode requiring advanced skills.
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture can be adjusted to optimize image quality in various lighting conditions. Flight limits can be set to restrict the drone’s operational area for safety.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The drone camera is a key feature for many users. This section covers camera operation and techniques for capturing high-quality images and videos.
Camera Features and Functions
Drone cameras typically offer various features including high-resolution video recording, still image capture, adjustable aperture, shutter speed, ISO, and often, electronic image stabilization. Some may include advanced features like HDR (High Dynamic Range) and panorama modes.
Camera Settings Adjustments
Adjusting ISO, shutter speed, and aperture allows for control over exposure, depth of field, and motion blur. Experimentation and understanding of these settings are crucial for optimal image quality. Higher ISO values are better for low-light situations but can increase noise. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
For high-quality photos, use a stable platform (a gimbal is highly recommended), ensure proper lighting, and experiment with different settings to find what works best. For videos, maintain smooth, controlled movements and avoid sudden changes in direction or speed.
Composing Effective Aerial Shots
Effective aerial shots often involve planning the composition and considering elements like leading lines, rule of thirds, and the overall perspective. Experiment with different angles and viewpoints to capture unique and compelling visuals.
Drone Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care is crucial for extending the lifespan and performance of your drone battery. This section covers safe charging and storage practices.
Battery Care and Maintenance
LiPo batteries require careful handling. Avoid overcharging, discharging, or exposing them to extreme temperatures. Store them in a cool, dry place at around 50% charge when not in use. Regularly check for physical damage, swelling, or other signs of degradation.
Safe Charging and Storage
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger. Never leave batteries unattended while charging. Store them in a fire-resistant bag or container. Avoid extreme temperatures during both charging and storage.
Factors Affecting Flight Time
Flight time is influenced by factors such as battery capacity, drone weight, flight style (aggressive maneuvers consume more power), wind conditions, and temperature. Colder temperatures reduce battery performance.
Recognizing Battery Degradation
Signs of battery degradation include reduced flight time, increased charging time, swelling of the battery, and unusual heating during charging or operation. A degraded battery should be replaced immediately.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues

This section identifies common drone malfunctions and provides troubleshooting steps.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Various issues can arise, from simple problems to more complex ones. Addressing them promptly and correctly is vital for continued safe operation.
- Motor Failures: Inspect motors and propellers for damage. Check motor connections and power supply.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure a clear view of the sky. Try recalibrating the GPS module.
- Low Battery: Check battery charge and health. Replace or recharge as needed.
- Flight Controller Issues: Try restarting the drone. If the problem persists, seek professional assistance.
- Gimbal Malfunctions: Check gimbal connections and power supply. Calibrate the gimbal.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions, How to operate a drone

| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution | Preventative Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Check battery, replace battery, check power switch | Regularly check battery health |
| GPS signal lost | Obstructions, interference, weak signal | Find a clear area, recalibrate GPS | Fly in open areas |
| Propeller malfunction | Damaged propeller, loose propeller | Replace damaged propeller, tighten propeller | Regularly inspect propellers |
| Erratic flight | Calibration issues, sensor problems | Calibrate sensors, check for sensor damage | Regularly calibrate sensors |
Drone Laws and Regulations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. This section provides a summary of key considerations.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
- Registration: Many jurisdictions require drone registration.
- Airspace Restrictions: Avoid flying near airports, restricted airspace, or populated areas without proper authorization.
- Flight Limits: Adhere to altitude and distance limitations.
- Privacy Concerns: Respect privacy laws and avoid filming people without consent.
- Safety Guidelines: Maintain visual line of sight, and operate responsibly.
Always check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations in your area. Ignorance of the law is not a defense.
Successfully operating a drone requires a blend of technical understanding, practical skill, and adherence to safety regulations. This guide has provided a foundational framework for mastering drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvering techniques and legal considerations. By diligently following the procedures Artikeld, you can confidently and safely explore the exciting world of aerial technology. Remember to always prioritize safety and responsible drone operation.
Quick FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and ample online tutorials.
How do I obtain necessary permits and licenses for drone operation?
Drone regulations vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements and licensing procedures. Registration may be mandatory.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If GPS signal is lost, immediately switch to a more stable flight mode (if available) and carefully bring the drone down to a safe landing. Avoid sudden maneuvers.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’re operating in areas with significant magnetic interference.
What are the signs of a failing drone battery?
Signs of a failing battery include reduced flight time, erratic behavior during flight, and physical damage such as swelling or leaking.
